Possible Complications and Nursing Analysis of Clinical Use of Disposable IV Catheters
Essential or Meaninful Learning Documents!
Possible Complications and Nursing Analysis of Clinical Use of Disposable IV Catheters
The application of disposabl IV catheter is a better method for clinical infusion. On the one hand, it can alleviate the pain caused by repeated scalp needle puncture in infants and can be suitable for adults undergoing long-term infusion. On the other hand, it also reduces the workload of clinical nurses. However, during the use of IV Catheter, there may be a certain probability of complications due to individual differences and nursing factors.
This article collects and organizes the possible complications and nursing analysis of IV Catheter in clinical use, and shares them with everyone to learn together.
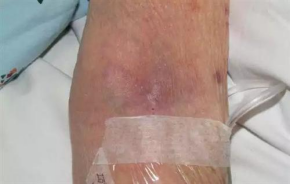
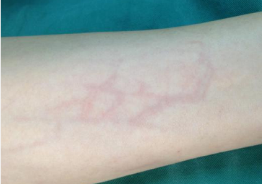
Clinical symptoms: Pain, swelling, and tenderness with cord like or bead like nodules
Common causes: intravenous administration of highly irritating, high concentration drugs, or prolonged use; Superficial varicose veins, obesity, smoking, trauma; bacterial infection.
Routine processing:
- Immediately remove the catheter and raise the affected limb to promote venous reflux and alleviate symptoms.
2. Local topical drugs, such as Xiliao Tuo ointment, nitroglycerin patch, anisodamine, etc., as well as magnesium sulfate or potato slices wet compress.
3. New dressings such as hydrocolloid transparent patches also have good effects
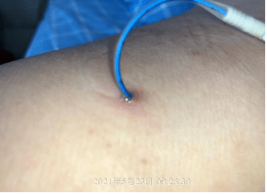
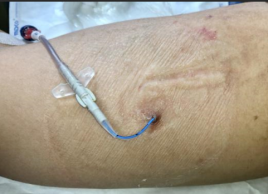
Clinical symptoms: Pain, swelling, fever and other symptoms at the injection site, purulent secretion at the puncture point, and increased body temperature.
Common causes: improper operation of sterile technology; Pollution of items; Failure to replace the application in a timely manner due to sweating, bleeding, and fluid leakage.
Routine processing:
1、When infection occurs, first apply disinfectant to the local area, wait for 2 minutes before removing the needle, and then press with sterile patches. Collect exudate and submit for inspection if necessary. Follow medical advice for medication and symptomatic treatment.
2、On the basis of routine disinfection, use iodophor therapy to reduce 2cm × After soaking a 3cm 4-layer sterile gauze in 1% iodophor, use tweezers to twist it until there is no dripping. Cover the puncture point with iodophor gauze, then cover it with 2 layers of dry sterile gauze, and finally apply a transparent film to cover it.
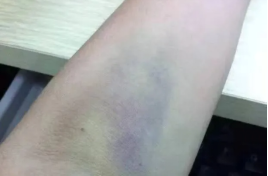
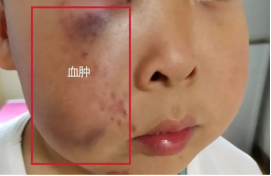
Common symptoms: The skin around the injection site changes color, showing a cyan color, and there may be swelling in the local area.
Common causes: Inadequate manipulation, needle penetration through blood vessel wall, incorrect pressing method after needle extraction, resulting in blood leakage. Especially for elderly people, patients with brittle blood vessels, excessive weight loss, and coagulation disorders or the use of anticoagulants.
Routine processing:
Mild hematoma does not need to be treated and can be absorbed on its own; Cold compress for large hematoma is suitable for use within 24 hours, and hot compress is suitable for use within 72 hours.
Common symptoms: Local redness, swelling, pain, painful bloody hard strips or beaded nodules.Common causes: Infusion of irritating drugs and solutions; Damage to veins during needle puncture.
Routine processing:
1. Rest in bed, lift the limbs slightly above the level of the heart; Try to prioritize upper limb venipuncture and avoid lower limb puncture.
2. According to clinical conditions and medical advice, medication should be used to strengthen the protection of venous vessels. Patients in the acute phase should use vasodilators, anticoagulants, and thrombolytic drugs, while patients with fever should receive antibiotics.